Technology has revolutionized nearly every aspect of our lives — from work to school to entertainment. Classrooms must stay up to date to keep students engaged and support their growth as modern learners. Many students say they lose focus during conventional lessons that lack creativity and interaction. By introducing fresh teaching tools and techniques, you can revitalize your classes. This guide to innovative teaching will give you nine ideas to modernize your classroom for an engaging learning experience.
What makes teaching innovative?
Innovative teaching means more than buying the latest technologies, though these can be helpful tools. Innovative teaching is about finding fresh ways to enhance the learning process for every student.
By nature, innovative teaching adapts to different classes and brings out a teacher’s creativity. That means the best innovative approaches for one class may be different from another. But common features of innovative teaching approaches include:
- A student-centered approach: Innovative teaching is always willing to revisit an approach to see if it works best for the students. The focus is on increasing student engagement, interaction, collaboration, and internalization of the material. Innovative teachers will leave their own comfort zones to explore new ways of achieving these goals for their students.
- Awareness of individuality: Innovative teaching celebrates diversity over conformity. While the whole class needs to meet certain standards, each person’s route could be a little different. Innovative teachers are more aware of the different learning preferences, styles, and abilities in their classrooms. They’re eager to adapt teaching to these varying needs through techniques like self-guided work and adaptive learning.
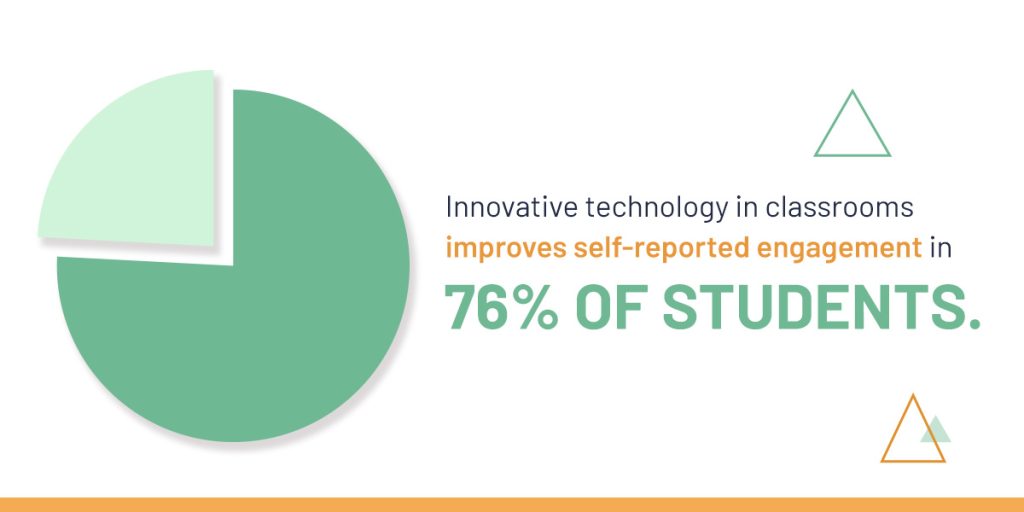
- Integration of technology: Innovative teaching uses technology to engage students and enhance understanding. Rather than incorporating gadgets for their own sake, the focus is always on using digital tools to help students internalize the curriculum. Innovative technology in classrooms improves self-reported engagement in 76 percent of students.
- Anchoring in reality: Innovative teaching ties concepts to real-world applications and examples. Career readiness is especially important, as 80 percent of college students consider this their key success indicator. Since learners are studying with careers in mind, making explicit connections to work situations can encourage engagement. On the other hand, engagement tends to drop off when students don’t see the real-world relevance of lesson content.
- Emphasis on problem-solving: Innovative teaching recognizes that the ability to figure out novel problems is as vital or more so than knowing any given set of facts. Creative problem-solving is becoming the most valuable human contribution in today’s economies, as memorization and computation are outsourced to machines. Innovative teachers train students in these high-value abilities by emphasizing practical problem-solving, creativity, and critical thinking over rote learning.
Why should I use innovative teaching in my class?
If you are considering incorporating more elements of innovative teaching into your classes, the most important consideration is how this will affect your students. After all, a student-centered approach is only worth adopting if it really helps the students! Here are six ways innovative teaching tools and techniques support student success:
- Research practice: Innovative approaches encourage self-guided research about new topics. This develops curiosity and independent research skills, which are valuable at every level of education, work, and self-formation.
- Enhanced critical thinking: Creative teaching techniques invite students to brainstorm and test solutions to fresh challenges in practice rather than waiting to receive prescribed answers. This helps learners build confidence in critical thinking and problem-solving.
- Improved internalization: Fresh teaching styles break material into smaller portions for students to digest through interaction before moving on to more chunks of information. This fosters confidence, internalization, and manageable pacing.
- Enriched soft skills: Interactive, collaborative learning approaches challenge students to sharpen crucial soft skills. These include time management, prioritization, communication, teamwork, leadership, and conflict resolution.
- Personalized learning: Adaptive learning technologies, individualized teaching, and self-assessment help to meet diverse learning needs. Students learn to recognize their gaps in understanding and take the initiative to address them, while teachers adapt their approach as they get to know each student’s learning style. The result is a tailored learning experience for each student to ensure they’re ready to progress.
- Increased engagement: Inventive teaching styles are more effective at inspiring participation and holding interest. This dynamic learning context gets students excited to engage with material on a deeper level. This increased motivation from introducing innovative methods and technologies can improve academic performance and even mental health.
What could Watermark do for your institution?
9 innovative tools and techniques to engage students
If you want to unlock the benefits of innovative teaching for your classes, the range of possibilities is vast and constantly expanding. But here are nine ideas that have been effective in real classrooms. Let them inspire you to explore the world of innovative teaching further for yourself as you discover what works best for your students.
1. The ripple method
The ripple method encourages students to respond to questions or prompts in three stages:
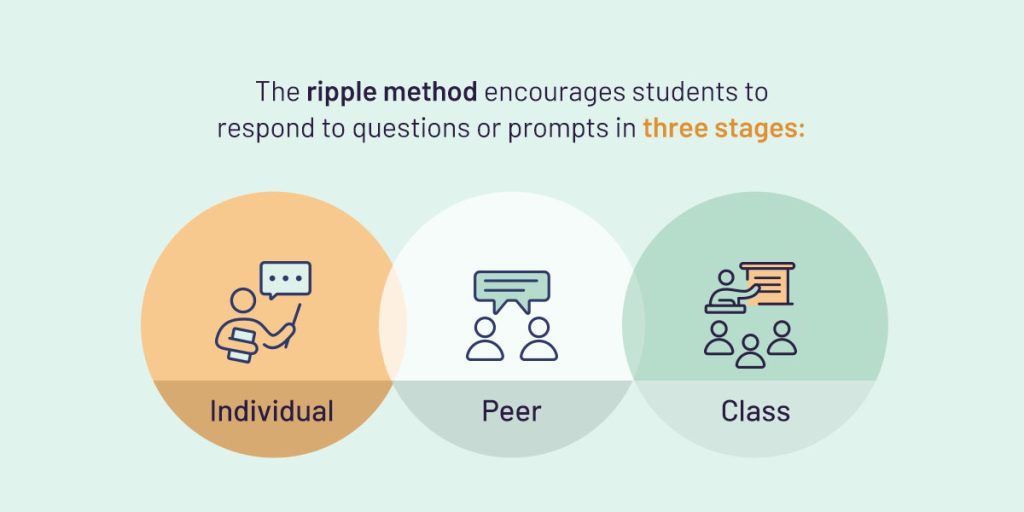
- Individual: First, students respond independently, in mind or in writing.
- Peer: Second, the students share their responses in small groups of up to four peers.
- Class: Third, the teacher invites volunteers to share their thoughts with the class.
The ripple method is an effective way of promoting interaction in class. Rather than immediately asking students to raise their hands and share with everyone, the teacher builds up to that moment. This gives students time to formulate and refine their responses through interaction, generating greater confidence and willingness to participate.
2. Project-based learning
Project-based learning (PBL) introduces students to a new concept and then asks them to find a real-world problem related to that concept and devise a solution. PBL goes beyond the conventional use of projects as a summative assessment method at the end of a course. Instead, PBL is a formative assessment approach in which the project is the teaching tool.
While students have substantial autonomy in PBL, the teacher still plays an important role. You become a coach, helping students find gaps in their approach to a project and sharing helpful resources. You aim to support them as they drive their own discoveries.
PBL is an active, engaged learning style that helps students improve their research skills, critical thinking, and problem-solving. This approach’s real-world practicality helps motivate students by showing them the relevance of the learning material. Often, PBL involves group collaboration, giving students a chance to practice their soft skills as well.
3. The jigsaw technique
The jigsaw technique is a collaborative learning approach that challenges students to understand concepts well enough to teach them to others. The jigsaw approach has 10 steps:
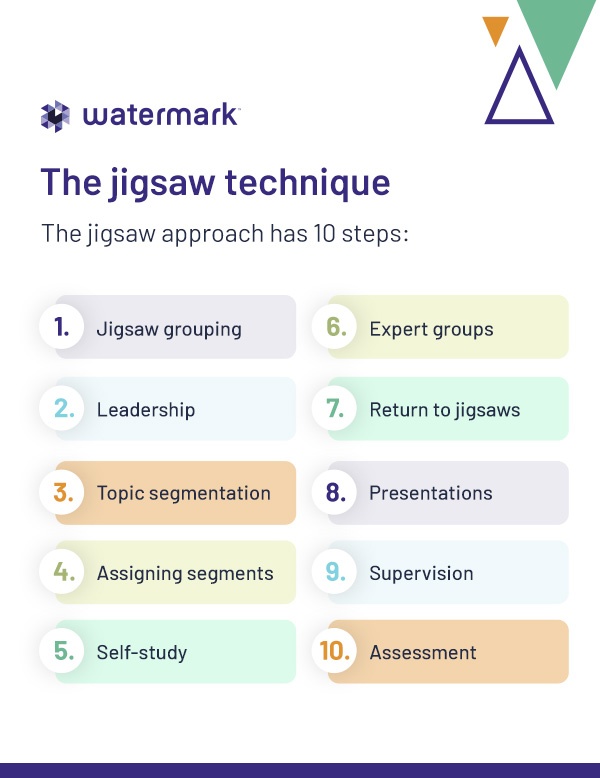
- Jigsaw grouping: Divide students into “jigsaw” groups of five or six. Aim for groups diverse in race, ethnicity, ability, and gender.
- Leadership: Appoint the most mature student in each group as the initial leader.
- Topic segmentation: Divide the lesson content into five or six segments. For example, you could divide a history lesson on Victorian England into Victorian politics, economics, sociology, arts, and philosophy.
- Assigning segments: Assign each segment to one student in each group. Only give students access to the material on their content segment.
- Self-study: Give students time to read and digest the material on their segment.
- Expert groups: Rearrange students into temporary “expert” groups with others assigned to the same segment. They discuss their main points and prepare to present the material to their “jigsaw” groups.
- Return to jigsaws: Return students to their “jigsaw” groups.
- Presentations: Ask each student to present their segment to the group, encouraging their peers to ask questions.
- Supervision: Float between groups as an observer, checking presentations for accuracy and interactions for fairness. If any domineering or disruptive behavior emerges, guide group leaders to intervene and only intervene yourself if necessary.
- Assessment: Present the entire class with an assessment covering all lesson segments.
This method improves student engagement, performance, and appreciation for diversity.
4. Educational apps
Faculties can explore various educational apps for mobile, tablets, and computers. Educational apps provide a wide range of functions:
- Integration with educational gaming, virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and other technologies.
- Streamlined assessment and progress data analysis functions for teachers.
- Multimedia content, including text, pictures, and video.
- Adaptable user experiences for students with diverse abilities.
- Compatibility with virtual and hybrid learning situations.
- Support for real time virtual collaboration between students.
Apps that have already transformed many classrooms include cloud-based collaborative document apps, quiz apps, virtual teaching platforms combining video with blackboards and media-sharing functions. A Learning Management System (LMS) can integrate these apps and track student progress, supporting customized learning pathways.
5. Educational games
Educational games are a subset of applications and programs that add an element of fun. Gamified learning improves student engagement and motivation through fun, even when the content is challenging. These games often use storytelling, puzzles, or role-play to make the learning experience more rewarding. Some incorporate humor, which many students find beneficial for learning.
Beyond the digital realm, teachers can also foster social confidence among peers as a prelude to collaborative projects through icebreaker games at the beginning of a course. “Find someone who…” is a fun example. The teacher creates a nine-block grid and fills each block with instructions to find a person with a different characteristic. For example, “find someone who is a morning person.” Students write down the name of a classmate who fits each characteristic in that block, aiming to find a name for each block within the time limit. This helps students learn each other’s names, making collaborating easier in subsequent sessions.
6. Virtual reality
Virtual reality (VR) is one of the most exciting ways to use technology to engage students. Along with virtual experiments and educational games, VR makes it possible to take students on virtual field trips.
Without leaving the classroom, students can have 360-degree interactive encounters with historical landmarks, distant ecosystems, and outer space. For example, a biology class in Pennsylvania can slip on their VR headsets and explore ecology in the Sundarbans mangrove forest of Bangladesh. VR provides many of the benefits of physical field trips in less time, without the hazards, and at a fraction of the cost.
Another exciting VR application is in remote or hybrid learning situations. Teachers and students can collaborate in immersive virtual spaces, offering a greater sense of presence and shared experience than other remote learning situations.
7. Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) has several capabilities that can enhance student engagement and understanding:
- Analyzing student performance data to identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Adapting content pacing, difficulty, and focus to address the needs of individual students.
- Assisting with revision and clarifications, much like a virtual tutor.
- Automating assessment and administration to streamline teacher workflows.
8. Adaptive learning
Innovative teaching aims to open different pathways for individual students to reach the same destination at their own pace. One student may only need three exercises to show confidence in a skill that takes another student 10 opportunities to understand. Adaptive learning software harnesses algorithms and often AI to tailor instruction to each student’s needs. This usually involves altering the question selection to address weaknesses before the student moves on.
While AI software can generate personalized learning experiences for many individual students in real time, innovative human teachers must be adaptive in their own right. Innovative teachers recognize the diversity of abilities and learning styles in their classes and aim to communicate with each student in ways that meet their individual needs. The teacher can view student progress data from the adaptive learning program to inform their approach. But by leaning into their emotional intelligence and empathy, a sensitive teacher can also get to know and respond to students as whole individuals in ways an algorithm can’t.
Benefits of adaptive learning include:
- Helping students gauge their level of understanding as they progress at their own pace.
- Promoting engagement through personalized learning.
- Capturing progress data for teachers to evaluate how instruction prepares students for assessment.
- Flagging students struggling in certain areas early so teachers can provide support.
9. Spaced repetition
Spaced repetition is most popular for learning vocabulary, but it is effective for memorizing anything. Its principles are:
- The tool: Physical flashcards are a classic tool, but flashcard apps are more efficient in storing large amounts of information and automating review intervals.
- The information: The review content could be any small portions of information, like vocabulary, facts, or formulas.
- The intervals: Learners start with a default interval, like reviewing each flashcard once per day. Depending on their accuracy, this interval becomes longer or shorter.
- The habit: Spaced repetition is most effective for students who use it consistently for an extended period.
Adopt an innovative assessment system with Watermark
Innovative teaching capitalizes on fresh tools to engage students in their academic growth. From project-based learning and jigsaw sessions to the latest advances in AI and VR, the focus is always on serving your students.
At Watermark, we offer innovative software solutions to streamline assessment, collect student progress data, and drive ongoing improvement. The Watermark Educational Impact Suite (EIS) provides a centralized hub for all your assessment data. This enables automated analysis of student performances across assessments, supporting adaptive teaching.
Request a demo to discover how Watermark can help your institution and students succeed.